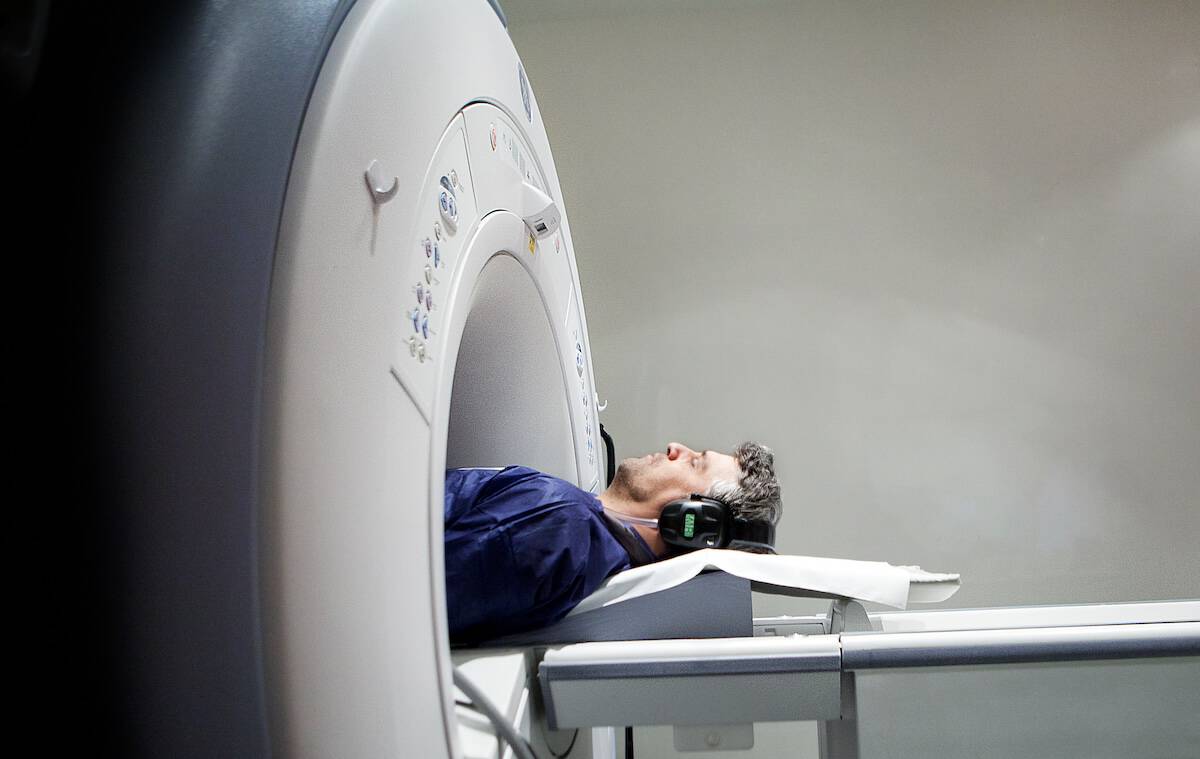
A more comfortable MRI with shorter scan times
With shorter scan times and highly-trained physicians to interpret your images, we ensure the most accurate results so you can get back to what matters most —your health.
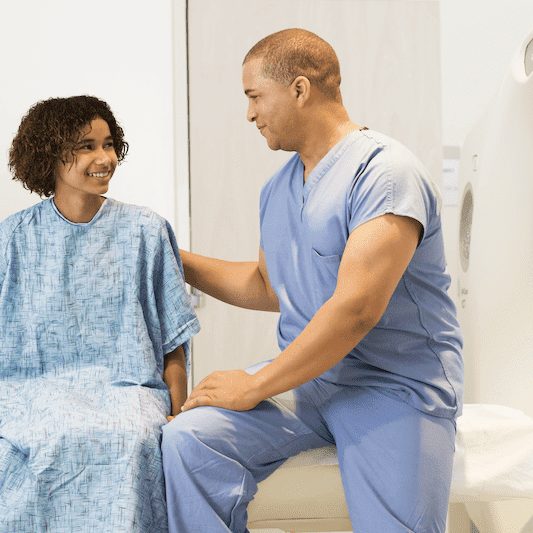


Our technologists' kind and compassionate care are why our patients continue to choose us for their MRI needs. Patient care and expertise matter, which is why our techs continue to develop their skills with advanced training.

Jefferson Radiology is recognized as an Accredited Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Facility by the American College of Radiology.
We designed a multi-step process to ensure the highest standards of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) safety for every patient. Our best practice safety measures include our multi-step screening questionnaire and metal detection process. As a result, we can now safely accommodate patients with stimulators.


Interventional Radiology860-676-0110
Vein Center860-293-7330
More InformationMRI produces photos of the inside of your body using magnets and radio waves. Different tissue characteristics are translated into different contrast levels on the image. A typical procedure averages 30-45 minutes, depending on the type of information required by your physician. You can help to make your images as clear as possible by relaxing and remaining still during the exam. Some patients even fall asleep during their MRI exam.
MRI is important because the scans help diagnose and monitor patients accurately while producing detailed images for your doctor to make the best decisions about your care plan. MRI can show the difference between healthy and diseased tissue and provide important information about the brain, spine, joints, and internal organs. It can lead to early detection and treatment of disease and has no known side effects.
While most exams do not have requirements, some may need you to fast a few hours before the exam. Your doctor will give you instructions if that is necessary. You will be asked to remove items that are incompatible with the magnetic field, like implants or similar items. Check with your physician or MRI technologist if you have had any brain, ear, or eye surgeries or any of the following: Pacemaker, neurostimulators (TENS unit), metal implants, Intrauterine device, Aneurysm clips, surgical staples, implanted drug infusion device, foreign metal objects in the eye or permanent eyeliner.
Once the exam begins, you will hear a knocking sound representing changes in the magnetic field. This sound is a normal part of the imaging process. We offer headphones during the exam to provide you with a more peaceful experience.
No, an MRI itself does not hurt. However, lying still for an extended period can become uncomfortable, and some people might feel claustrophobic inside the MRI machine. It’s important to talk to your doctor before your exam if you feel you may be uncomfortable. Additionally, you’ll receive a call button to hold onto before the exam is started. It will allow you to maintain two-way communication with the technologist during the exam.
During your MRI exam, a technologist can always see you. For your convenience, an intercom system is built into the MRI so you can communicate with the technologist anytime. A contrast agent may be administered in certain instances to enhance the study. There are no extra precautions for the contrast (if required), but you can consult your physician or technologist if you have any questions. You should also inform the technician if you have any metal implants, tattoos, or if there’s a possibility you’re pregnant.
While both MRI and CT scans produce cross-sectional images of the body, MRI uses strong magnets and radio waves, whereas CT uses X-rays. MRI is better for viewing soft tissues, while CT is typically better for viewing bones.
Not always. The part of the body being imaged will be centered in the magnetic field. However, for imaging areas like the spine or brain, most of your body might be inside the machine.
When your referring doctor says they have reviewed your MRI results, that usually means they have reviewed the imaging exam with a radiologist. An MRI radiologist is a medical doctor specialized in reading and diagnosing MRIs. The radiologist reading your MRI is like an expert counselor to your doctor who sent in your order for the MRI. The radiologist aids your doctor in choosing the best exam you need, interpreting the radiology exam, and relaying the test results to your doctor to plan your care.